Skin Lightening
The Model
MatTek's MelanoDerm™ System consists of normal, human-derived epidermal keratinocytes (NHEK) and melanocytes (NHM) which have been cultured to form a multilayered, highly differentiated model of the human epidermis. The NHM within co-cultures undergo spontaneous melanogenesis leading to tissues of varying levels of pigmentation. The tissues are produced using serum free medium without artificial stimulators of melanogenesis such as TPA and IBMX. The cultures are grown on cell culture inserts at the air-liquid interface, allowing for topical application of skin lighteners or self-tanning agents, providing a useful in vitro means to evaluate cosmetic and pharmaceutical agents designed to modulate skin pigmentation. For more information on MelanoDerm, click here.
APPLICATION NOTE
In Vitro Evaluation of Cosmetic Ingredients and Formulations for Skin Lightening using MelanoDerm
Objective
To evaluate skin lightening following treatment with topically or systemically applied cosmetic ingredients and formulations by measuring macroscopic darkening and melanin
Methods
MelanoDerm tissues (Figure 1) were produced in the MatTek Corporation GMP tissue production facility .
25μl of each ingredient or formulation was applied topically to the MelanoDerm tissues every other day for up to 14 days.
After treatment, MelanoDerm tissues were processed for macroscopic imaging and melanin analysis.
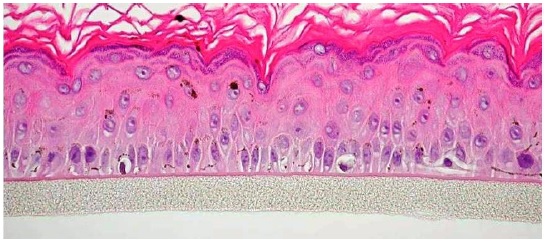
Figure 1. Histology of MelanoDerm. H&E stained cross-section
showing that the tissue morphology of MelanoDerm closely parallels
that of normal human skin. The epidermis contains basal, spinous,
granular and stratum corneum layers and functional human
melanocytes (400x).
Results
Progressive skin darkening (Figure 2) and melanin production (Figure 3) were observed in untreated control tissues.
Treatment of the MelanoDerm tissue model with known lightening ingredients of commercially available dark spot corrector formulations caused macroscopic skin lightening
(Figure 2) and a reduction in melanin production (Figure 3) compared to untreated controls.
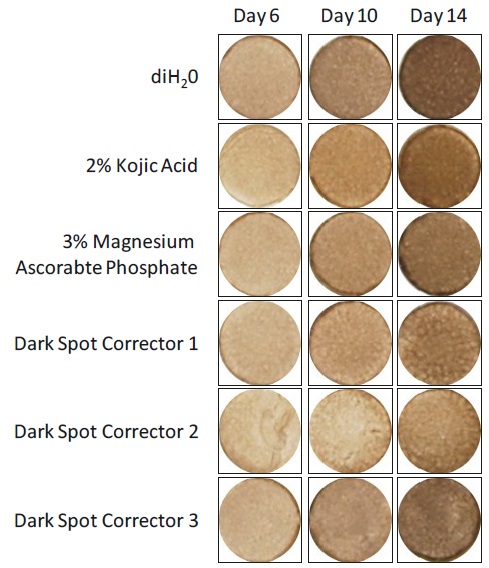
Figure 2. Effect of cosmetic ingredients and formulations on
macroscopic darkening in the MelanoDerm tissue model.
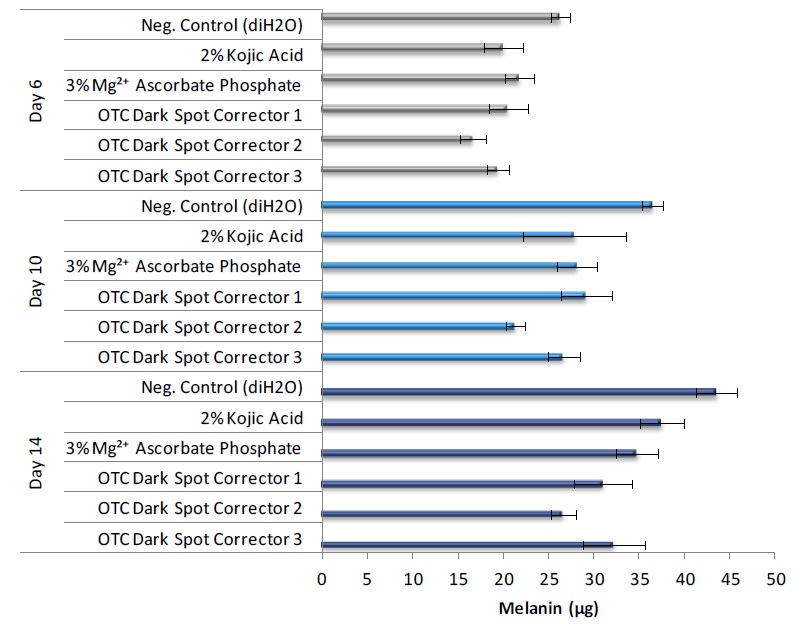
Figure 3. Effect of cosmetic ingredients and formulations on melanin production in the MelanoDerm tissue model.
Conclusion
Assessment of skin lightening following treatment with topically or systemically applied cosmetic ingredients or formulations in the MelanoDerm in vitro human skin model can be used in efficacy and claims substantiation studies.
Additional applications for the EpiDerm, MelanoDerm and EpiDermFT tissue models include Anti-aging, Skin Whitening, and UV Protection.
Technical References

720. SCREENING OF PLANT EXTRACTS FOR HUMAN TYROSINASE INHIBITING EFFECTS. Kim1, M., Park1, J., Song1, K., Kim2, H.G., Koh2, J.-S. and Boo1, Y.C. 1Department of Molecular Medicine and Cell and Matrix Research Institute, BK21 Medical Education Program for Human Resources, Kyungpook National University School of Medicine, Daegu and 2Dermapro Skin Research Center, Dermapro Co. Ltd., Seoul, Korea. Inter. J. of Cosmetic Science, 34, 202–208 (2012).
717. FORMULATION OPTIMIZATION, SKIN IRRITATION, AND EFFICACY CHARACTERIZATION OF A NOVEL SKIN-LIGHTENING AGENT. Jain1, P., Sonti2, S., Garruto2, J., Mehta2, R., & Banga1, A.K. 1Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences, Mercer University, Atlanta, GA, USA. 2SkinMedica Inc, Carlsbad, CA, USA. J. of Cosmetic Derm., 11, 101–110 (2012).
601. INHIBITORY EFFECTS OF Á-ARBUTIN ON MELANIN SYNTHESIS IN CULTURED HUMAN MELANOMA CELLS AND A THREE-DIMENSIONAL HUMAN SKIN MODEL. Sugimoto1, K., Nishimura1, T., Nomura1,K., Sugimoto2, K., and Kurikia1, T. 1Biochemical Research Laboratory, Ezaki Glico Co., Ltd.; Osaka, Japan and 2Laboratory of Applied Molecular Biology, Division of Applied Biochemistry, Graduate School of Agriculture and Biological Sciences, Osaka Prefecture University, Osaka, Japan. Biol. Pharm. Bull., 27, 4, 510-514, 2004.
504. 1-(2,4-DIHYDROXYPHENYL)-3-(2,4-DIMETHOXY-3-METHYL-PHENYL)PROPANE, A NOVEL TYROSINASE INHIBITOR WITH STRONG DEPIGMENTING EFFECTS. Nesterov1, A., Zhao1, J., Minter2, D., Hertel1, C., Ma1, W., Abeysinghe1, P., Hong1, M., and Jia1, Q. 1Unigen Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; 2660 Willamette Drive NE, Lacey, WA 98516, U.S.A.: and 2Chemistry Department, Texas Christian University; Fort Worth, TX 76129, USA. Chem. Pharm. Bull., 56(9) 1292-1296 (2008).
264. RESULTS USING MELANODERM™, AN EPIDERMAL MODEL CONTAINING FUNCTIONAL MELANOCYTES, DEMONSTRATE EFFICACY OF NOVEL SKIN LIGHTENING FORMULATIONS. Klausner, M., Kubilus, J., Hayden, P.J., Last, T.J., DePaoliAmbrosi*, G. MatTek Corporation, Ashland, MA, *General Topics, s.r.l., San Felice del Benaco, Italy. Presented at Soc. Invest. Derm. Meeting, May (2002).




www.MatTek.co.kr